Agentic AI, Part 1
Introduction
Agentic AI refers to intelligent systems that plan, decide, and act to achieve user-defined goals. Unlike simple automations or purely generative systems that react to prompts, agentic systems operate proactively across multiple steps, integrating reasoning, planning, and tool use.
Human + Automation vs Agentic AI
Let’s walk through a relatable task and compare the flows.
Task: Reach home for Dad’s birthday.
Human + Automation Flow:
- [Human] Find destination (city + address).
- [Human + Automation] Find birthday (calendar, email, messages).
- [Human + Automation] Find arrival time (calendar, constraints).
- [Human + Automation] Plan route (maps, transit, flight search).
- [Human + Automation] Fetch flight and price options.
- [Human] Review options, select, reserve.
- [Human + Automation] Create/update calendar events (birthday, cabs, flight, home).
- [Human + Automation] Add reminder to buy a gift.
- [Human] Purchase gift and travel.
Agentic AI Flow:
- [AgenticAI] Determine destination (city + address).
- [AgenticAI] Retrieve birthday (calendar, email, messages).
- [AgenticAI] Determine arrival time (calendar, constraints).
- [AgenticAI] Plan route (maps, transit, flight search).
- [AgenticAI] Fetch flight and price options.
- [AgenticAI + Human] Present options, get selection, make reservations.
- [AgenticAI] Create/update calendar events (birthday, cabs, flight, home).
- [AgenticAI] Add reminder to buy a gift.
- [Human] Purchase gift and travel.
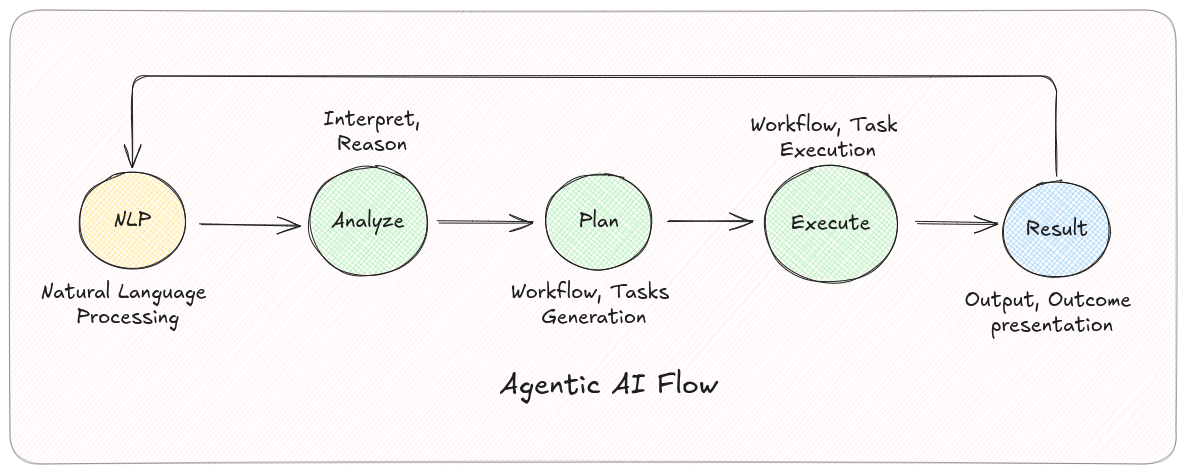
The Agentic AI Cycle
Agentic AI operates in a continuous loop of perception, reasoning, and action. User objectives are translated into executable plans.
- Context Perception: Gather and process data from databases, user input, APIs, sensors, etc., to understand the current context.
- Reasoning and Planning: An LLM acts as the “brain,” decomposing the goal into sub-tasks and sequencing a plan.
- Action: Agents execute the plan by calling tools and systems (APIs, MCP servers, code, browser automation, etc.).
- Learning and Reflection: Evaluate outcomes, refine strategies via feedback loops, and improve over time.
Agentic AI vs Other AI Systems
| Feature | Agentic AI | Generative AI | Traditional AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Autonomous, goal-oriented action and decision-making. | Create new content (text, code, images) from prompts. | Automate repetitive, specific tasks via predefined rules. |
| Autonomy | High — initiates and completes tasks with minimal supervision. | Low — reactive to user prompts. | Low — depends on fixed algorithms and triggers. |
| Workflow | Dynamic and adaptive; can course-correct. | Reactive and stateless; one request at a time. | Static and rule-based; brittle outside scoped parameters. |
| Planning & Reasoning | Multi-step planning, decomposition, and decision-making. | Limited explicit planning; mainly prompt-to-output. | No planning; executes predefined logic. |
| Tool Use | Integrates tools/APIs, external services, and automation to act. | Optional tool use via plugins/functions, typically within a single request. | Fixed integrations; scripted automations. |
| Memory/State | Maintains working memory and longer-term context for tasks. | Mostly stateless per request; limited session memory. | State handled via application code and databases; not adaptive. |
| Learning & Feedback | Reflects on outcomes; can self-correct via feedback loops. | No built-in reflection; improvements via retraining or prompt tuning. | No learning; behavior changes only via code/config updates. |
| Human-in-the-loop | Human sets goals and approves key decisions when needed. | Human crafts prompts and reviews outputs. | Human designs rules; minimal runtime interaction. |
| Typical Outputs | Completed tasks, updates to systems, and decisions taken. | Text, images, code, audio generated from prompts. | Deterministic actions within a narrow scope. |
| Example | Handles a support ticket end-to-end (verify, refund, update CRM). | Writes a marketing email or generates an image. | Scripted chatbot or a simple spam filter. |
Real‑world Use Cases
The adaptive, autonomous nature of agentic AI enables it across industries to handle complex, multi-step processes:
- Customer Service: Resolve complex inquiries end-to-end, from troubleshooting and assisting with purchases to issuing refunds.
- Financial Services: Detect and block fraud in real time by analyzing transaction streams.
- IT Service Management (ITSM): Resolve low-level tickets (password resets, access provisioning) using authorization rules.
- Software Development: Generate code, run tests, triage bugs, and submit PRs.
- Supply Chain: Reroute shipments, adjust inventory, and place restock orders dynamically.
- Healthcare: Assist with diagnostics from medical records and automate scheduling/administrative tasks.
Risks and Challenges
Agentic AI remains early; risks mirror broader AI concerns and introduce new ones:
- Privacy: Collection and use of personal data to provide services and improve performance.
- Security: Vulnerable to malicious use or compromise.
- Compliance: May not align with regulations without careful guardrails.
- Efficiency/Cost: Compute vs human trade-offs can make some tasks costly.
- Ecosystem: Integration with existing systems is non-trivial; MCP interfaces help, but gaps remain.
- Accountability: Assigning responsibility is hard; opaque reasoning hampers audits.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Memory poisoning, goal manipulation, or misuse of tools/data.
- Unintended Consequences: Poorly defined goals can lead to undesirable optimizations (e.g., risky trading).
- Data Bias: Biased training can produce discriminatory decisions.
- Integration Complexity: Connecting to legacy systems can be resource-intensive.
- Over‑reliance: Excessive trust reduces human oversight and error detection.
This is Part 1. In future parts, we will explore agent architectures, memory, tool interfaces (incl. MCP), and evaluation strategies.